Watch this webinar to learn about the metabolic changes during COVID-19 disease, how these can be accurately tracked and how NMR* can improve the clinical understanding of Long-COVID.
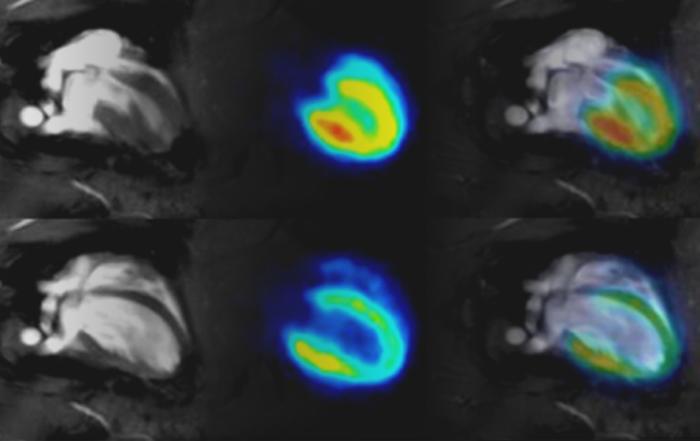
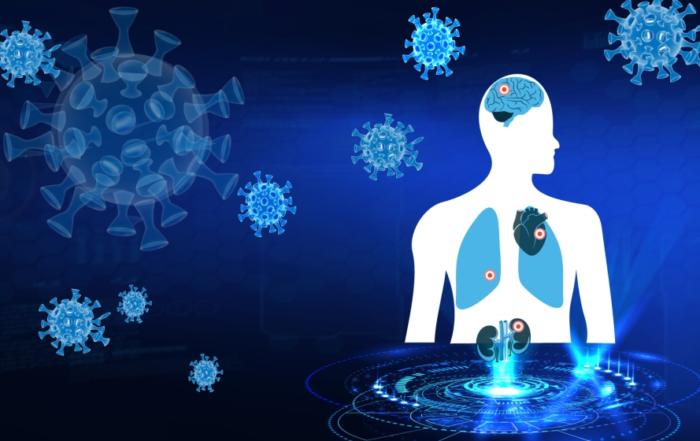
A better understanding of COVID is urgently needed in order to improve the management of long-term disease risks after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection at the individual and global healthcare level. More than 1 in 5 adult COVID survivors may develop long-term impairment, thus millions of patients suffer from PACS, also commonly known as Long COVID. PACS involves damage to a variety of organ systems (e.g. lungs, heart, kidneys, pancreas), along with mental health impairment. There is an emerging consensus in recent publications that an individual’s NMR* metabolomic signature delivers reliable insight into PACS. Thereby NMR* enables the study of SARS-CoV-2 triggered metabolic phenoconversion, defined as transient or persistent systemic change of the molecular signature in human blood after acute infection. Subsequent Phenoreversion, indicated by normalization of the metabolic signature, can be detected by NMR* and may mark PACS recovery.
The newly launched NMR*-based Bruker’s PhenoRisk PACS™ multi-organ risk screen enables in-depth monitoring of PACS in order to detect secondary disease as early as possible.
*The methods and solutions discussed during the webinar are for research use only and not for use in clinical diagnostic procedures
Key Topics Include:
- Understand the phenoconversion and phenoreversion concept in COVID disease
- Understand the metabolomic biomarkers involved in PACS/Long COVID
- Understand the recent publications on NMR*-based multi-organ risk screening in PACS
Who Should Attend?
- NMR* scientists
- Researchers studying COVID 19 disease
- Clinical trial investigators
- Clinicians