Experts discuss electrical and optical-based techniques capable of stimulating and recording neuronal activity during fMRI, share examples using these tools to study neurovascular coupling, and introduce a method to acquire fMRI data at zero echo time and discuss the advantages over traditional fMRI technique.
Given the increasing use of fMRI, studying neurovascular coupling is essential to better interpret what the fMRI signal means. It is also crucial to develop new fMRI techniques that can avoid anesthesia confounds, reduce distortion, and improve sensitivity.
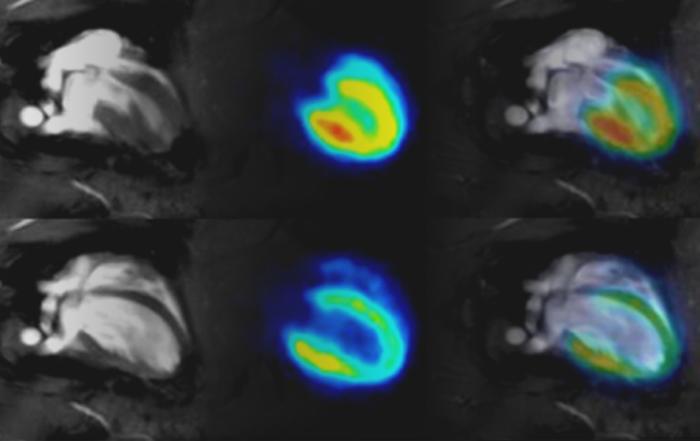
Dr. Ian Shih from the University of North Carolina (UNC) will begin this webinar by shedding light on the not always straightforward relationship between neuronal activity and hemodynamic responses. Shih will discuss techniques capable of stimulating and recording neuronal activity during EPI-based fMRI, including electrical deep brain stimulation, optogenetics, electrophysiology, fast-scan cyclic voltammetry, and optical fiber photometry, and share an example using these tools to study neurovascular coupling. The second half of the webinar will be led by rising scientist Martin MacKinnon, also from UNC, who recently won the Bruker Award, which Bruker announced during the ISMRM. MacKinnon will introduce the method to acquire fMRI data at “zero” echo time and discuss its advantages over traditional fMRI techniques.
This webinar will discuss neuromodulation and recording techniques that can be performed simultaneously with fMRI and demonstrate how these tools can be used to address a specific research question related to neurovascular coupling. Additionally, fMRI using zero echo time will be introduced and its strengths for fMRI applications will be demonstrated.
Who Should Attend?
This webinar is of interest to researchers wishing to solidify their knowledge about recording and stimulating neuronal activity during fMRI as well as those interested in conscious imaging, avoiding anesthesia confounds, reducing imaging distortion, and improving detection sensitivity.
Presenters
Director of the Center for Animal MRI
Neurology and Biomedical Engineering
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
PhD Student
Biomedical Engineering
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill