Secret Health Benefits of Being a Bat
How exactly are the Myotis bat genus able to host COVID-19, Ebola, and other infectious diseases, all while living into their early 30s? We describe particular infectious disease adaptations, inflammation suppression, and the longevity observed within this taxa.
A No-Brainer: Organoids for Neuroscience Research
Explore brain organoids: 3D models advancing our understanding of brain development and disorders, and shaping future treatments.
Pressure-Volume (PV) Loops: Overview and Applications
PV loops are widely used among cardiovascular researchers as well as countless other disciplines, but there seems to be a lack of educational resources about them. Here we dive into what PV loops are, when they are used, as well as some case studies and limitations.
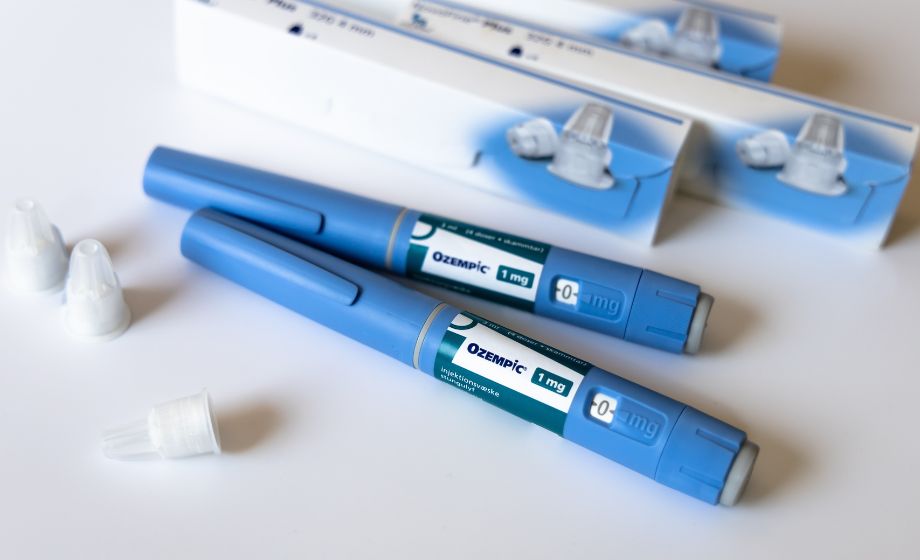
The Sweet Truth: Unwrapping the Science of Semaglutide
Semaglutide, also known as Ozempic and Wegovy, has become increasingly popular -- but why? Here we discuss the mechanism behind these drugs, how they've become so well known, and what current research says about their long-term effects.
Merging Minds and Machines: Recent Integrations of Brain-Computer Interfaces
Discover the future of human cognition with our overview of recent developments in brain-computer interface technology. Read this blog to find out how brain-computer interfaces function, ways they can be utilized, and how a few individuals have personally advanced this burgeoning neuroscientific field.
Taurine: An Unexpected Anti-Aging Ally
A recent publication from Singh et al. demonstrate how taurine, an amino acid used widely throughout the body, can improve age-related health outcomes in mice, roundworms, non-human primates, and also highlight how this effect appears to be evolutionarily conserved in humans.
Tick Tock: The Growing Risk of Lyme Disease and Efforts to Develop a Vaccine
In this blog we discuss Lyme disease, including reasons for increased prevalence, causes and symptoms, and vaccine developments.
What Does Exercise Do for the Brain?
While the overall benefits of exercise have been well documented, what exactly does exercise do for the brain? In this blog, we review two very recent publications that arrived at somewhat conflicting answers to this question.
Chronological Age vs Biological Age: Can Aging be Reversed?
What can biological age tell us about our health? Is it a fixed number, or can it be reduced? A recent study from Poganik et al. investigates the fluctuations in biological age in response to physiological stress.
How High-Impact Sports Affect Brain Health: Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a condition that arises from repeated head traumas, and can only be diagnosed after death. Learn more about the history behind this condition, current research, and potential ways to prevent CTE in this blog post, written by one of the Scientist.com STEM NIL Scholarship Winners.
CBD’s Potential as an Anti-Cancer Agent
Chemotherapy treatment is incredibly difficult on patient wellbeing, but an unlikely plant-derived substance may yet improve the adverse side effects. In this blog, we discuss the use of CBD as a treatment for side effects like organ damage and drug resistance in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy.
Can the Immune System Protect after Repeated Myocardial Injury?
While the immune response to a single cardiac event has been well researched, few have reported on whether an adaptive immunity is observed after repeated cardiac injury. Here, we discuss a recent publication from Tiwary et al., in which they investigate the cytoprotective response after multiple cardiomyopathic injuries.
From Trauma to Binge Eating: How Early Life Experiences Impact the Leptin System
Early life trauma (ELT) has been identified as a risk factor for binge eating and obesity in adult life, but the neural mechanisms behind this phenomena have yet to be determined. In this blog post we discuss a recent publication from Shin et al., which delineates the circuitry of this ELT-induced maladaptive eating.
A Breath of Not-So-Fresh Air: the Combined Effects of Air and Noise Pollution
While air and noise pollution have been well documented independently, their combined effects are insufficiently discussed, until recently. In this blog post, we discuss a recent publication from Kuntic et al. on the combined and individual effects of these pollutants in mice.
Cancer Immunotherapy: Viruses, Vaccines, and other Immuno-Oncology Treatments
In this blog post, current cancer immunotherapy treatments are discussed, as well as some future directions for this rapidly developing field.
Celebrating Black Scientists: 5 Scientific Stories from the Past
In honor of Black History Month, this blog discusses 5 scientific stories from some historic Black and African-American scientists, researchers, and medical professionals.
Protocol Preview: Long-read sequencing, Nature’s Method of the Year
Nature Methods declared "Long-Read Sequencing" their Method of the Year for 2022, but what exactly makes this technique worthy of such a title?
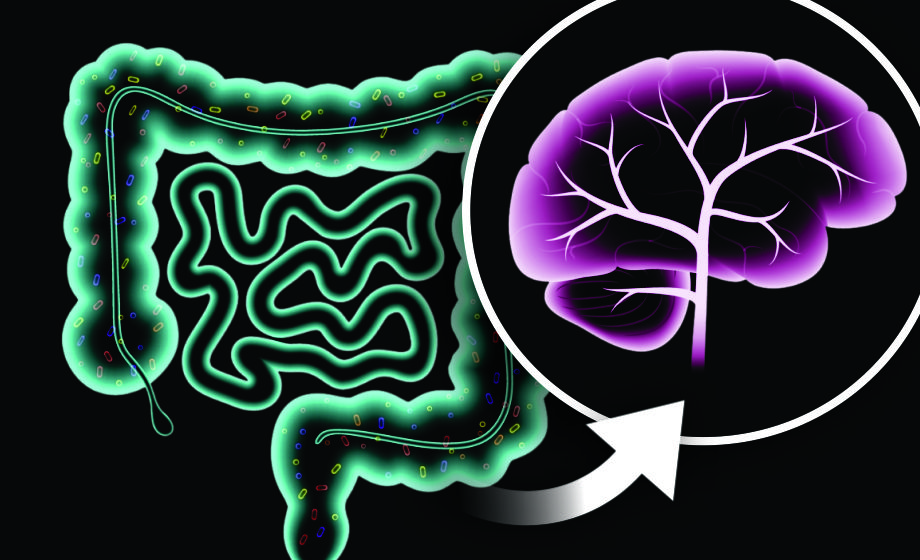
The Blues & the Browns: Links between Depression and Gut Microbiota
Recently, Radjabzadeh et al., identified 13 genera of gut microbiota that have been implicated with symptoms of depression.
Brain-Derived Tau in Blood: the Future of Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis?
Recently published in Brain, Gonzalez-Ortiz et al. report the design and development of a novel blood-based biomarker specific to brain-derived tau. In this blog post, we dive into the advantages of their novel immunoassay over those that are commercially available, as well as its future implications for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis.
Protocol Preview: In Vivo Gene Therapy Using Peptide-Based Delivery
Although gene therapy has been in discussion for decades, its translation to clinical practice has been a slow and challenging process. As a solution to this translational challenge, Allen et al. have proposed a peptide-based delivery method of Cre recombinase for in vivo gene therapy, which we review in this blog post.
Novel Targets for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment: Medin and PLD3
Given that Alzheimer's disease is multifactorial and heterogenous, drug development progress is more likely to occur if multiple pathways are considered. Two recent Nature publications have potentially identified medin and PLD3 as new targets for Alzheimer’s disease treatment, which we summarize in this mini-review.
A Novel Ingestible Biosensor for Intestinal Metabolite Monitoring
De la Paz et al. have developed an ingestible, self-powered, and wireless biosensing capsule that can hopefully be used for the noninvasive diagnosis of gastrointestinal disorders in the future. Recently published in Nature Communications, the authors demonstrated how its real-time performance in a porcine model, which we summarize in this post.
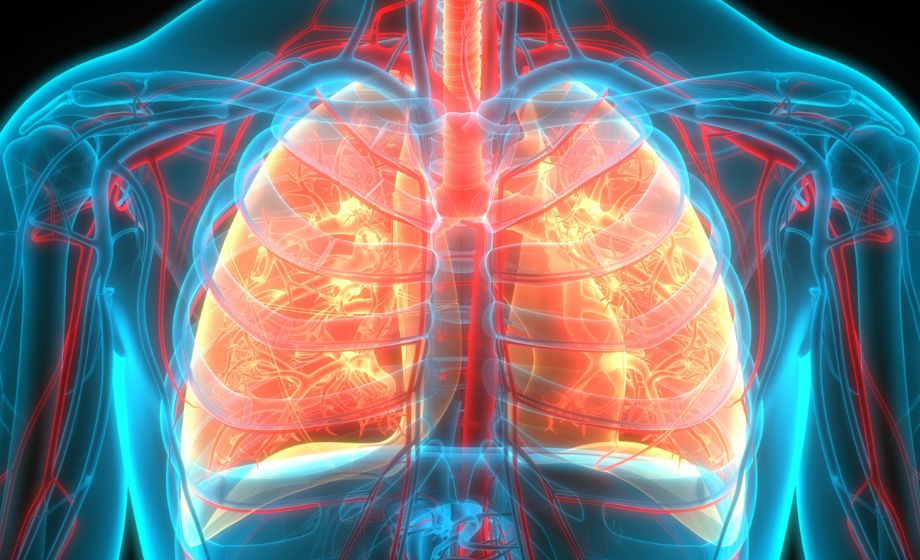
Particulate Matter from Firearms: Lung Toxicity and Respiratory Effects
While health and safety precautions are rightly focused on preventing shooting-related injury and death at firing ranges, heavy metal exposure also poses substantial health risks. Kim et al. recently modeled the acute health effects of particulate matter inhalation from firearm smoke in mice, which we review in this post.
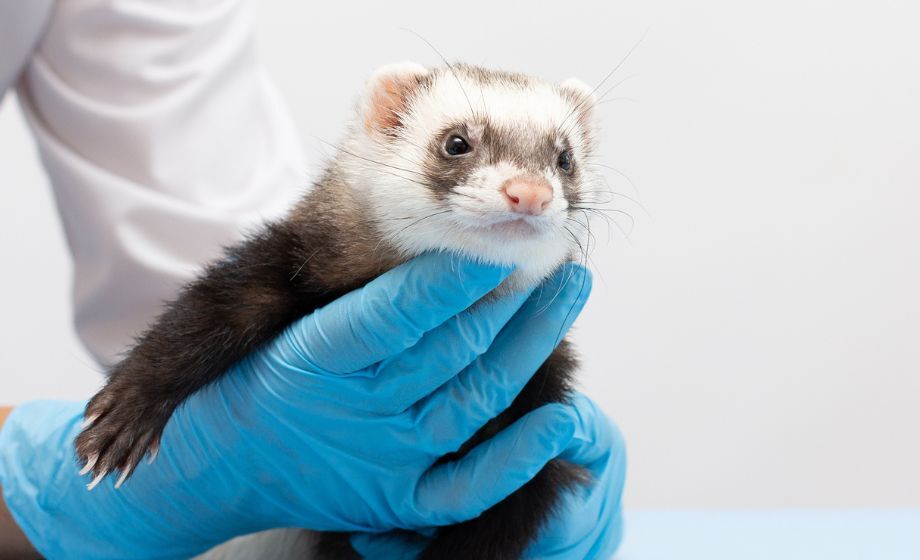
Protocol Preview: a Ferret Model of Respiratory Inflammation
While rodents have long been used to model many human diseases, their anatomical, physiological, and immunological differences from humans cannot be ignored when modeling respiratory inflammation. Recently, Khoury et al. demonstrated how ferrets can be used to model inflammatory respiratory disease and injury, which we review in this blog post.
Are They Born This Way? Beat Synchronization in Rats in Response to Lady Gaga, Mozart, and More
Recently, Ito et al. sought to understand beat synchronization in rats and how it compares to humans, which has not been reported to date. In this blog post, we review their findings and how they contribute to our understanding of cross-species beat synchronization.